Study on the Public Logistics Nodes of Industry Cluster District and Location
Tiantian Li1, a, Lu Qin2,b and Xijun Ge3,c
1Beijing Jiaotong University, China
2Beijing Jiaotong University, China
3Zhong Wu Xie(Beijing) Logistics Engineering Design Institute, China
a13120865@bjtu.edu.cn, bqinlu56@126.com, cgxijun@cledi.org.cn
Keywords: industry cluster district; public logistics nodes; multiobjective programming; location; layout
Abstract. The public logistics node was named. Through summarizing the logistics node on improving the current status of the industrial concentration, confirming the feasibility of building public logistics nodes and the huge advantages: reducing the empty driving, increasing the using of the warehouse, saving soil resources, enhancing the degree of enterprise specialization, promoting the enterprise's improvement. And using multiobjective programming gave the public logistics node location model.
Introduction
The characteristics of industry cluster district in our country: manufacturing enterprise cluster, less logistics supports; scattered layout of logistics. Especially in some big cities, because of the lack of land, it is so hard to equip the logistics facilities.
The public logistics node is built in industry cluster districts, which provides a unified transportation, storage and product processing services to each enterprise in the same industry cluster district. It helps the whole industry cluster district to supervise and coordinate the transportation, warehousing business.
Necessities of Building the Public Logistics Nodes
Reducing the Empty Driving Ratio. Through building the public logistics nodes in the industry cluster districts, the public logistics nodes can help to harmonize the import and export of every enterprise to make the management of all products and materials to be unified. The reasonable planning and the harmonization for every enterprise’s transportation and purchasing cycle will reduce down the rate of the empty driving. To management the transportation uniformly also can reduce down the transportation cost and the energy cost of the whole industry cluster districts.
Increasing the Utilization Ratio of the Warehouses. The decentralized management of warehouses should be changed to unified management, and coordinate every enterprises’ production cycle, which will help to increase the utilization ratio of the warehouses and reduce the cost of the warehouses’ management. The fast reactions can help to increase the production efficiency and the general strength of the whole industry cluster districts.
Saving the Soil Resource. If we can use the public logistics nodes to manage the logistics of all enterprises and to build the storage and logistics facilities uniformly, the used area of every enterprise for storage will be reduced down. When faced with the same requirements and the same quality for some products’ logistic, the public logistics nodes’ management will use the least area than other management mode, and the storage and logistic service level will be better than others. For these reasons, it was proved that to build the logistics nodes in the industry cluster districts can save the soil resource more effectively.
Enhancing the Degree of Enterprise Specialization. By building the logistics nodes in the industry cluster districts, we can manage the logistic of all enterprises uniformly. On the enterprises’ side, that means they can outsource more non-core businesses. Under this mode, the enterprises can concentrate much more on their core businesses, which can help to improve their professional levels and their competitiveness among other competitors.
Making a Strong Foundation for the Further Development. The paper puts forward several functions of public logistics nodes for the whole industry cluster district: Warehousing, transportation and reprocessing. The functions are based on the problems of industry cluster districts in our country. It can help to provide public services, so that the burden of enterprise development is reduced. It can also attract more enterprises, which, on the other hand, make the industry cluster district more powerful.
Sustainable Development Evaluation Model and Cost Minimization Model.
This model has two steps: firstly, comparing the benefits between the cluster management and the dispersive management to make sure that if it necessary to build up the public logistics nodes in the industry cluster districts. Secondly, based on the cost minimization model to confirm the best location of the public logistics nodes.
Sustainable Development Evaluation Model. The model analyzes the weights of economic benefits, social benefits and environmental benefits in public logistics node and the dispersive management. The model is based on the sustainability evaluation index system.
Determination of Project Benefit Value. The model comprehensively analyzes economic benefits(![]() ), social benefits(
), social benefits(![]() ), environmental benefits(
), environmental benefits(![]() ) and their weights(W).By comparing the total benefit value(SD) between two modes, we could make our decision.
) and their weights(W).By comparing the total benefit value(SD) between two modes, we could make our decision.
![]() ,
, ![]() (1)
(1)
Through questionnaires to experts, the value of W is:
The dispersive management: ![]() =0.5,
=0.5,![]() =0.3,
=0.3,![]() =0.2;
=0.2;
The cluster management: ![]() =0.2,
=0.2,![]() =0.4,
=0.4,![]() =0.4.
=0.4.
Determination of Analyzes Economic Benefits, Social Benefits, Environmental Benefits. The index system of comprehensive evaluation is based on feasible factors and questionnaires to experts. The index system is shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Index system
|
economic benefits( |
State macro control( |
|
Access to finance( |
|
|
Operational cost( |
|
|
rate of return( |
|
|
social benefits ( |
The impact on regional economic and social development( |
|
The ability to provide supporting facilities to other local economic activity( |
|
|
Improving public health( |
|
|
Land-use and its impact( |
|
|
Employment opportunities( |
|
|
environmental benefits( |
Ecological impact assessment( |
|
The impact of air( |
|
|
The impact of water( |
|
|
Construction noise( |
|
|
Environmental protection measures( |
|
|
Energy saving( |
The export score is calculated by functions:
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() (2)
(2)
These functions are kinds of triangle distribution. Maximum, minimum and the most possible values could be given by experts. Then using![]() ,
,![]() and
and ![]() instead of the value, when we build functions.
instead of the value, when we build functions.
![]() ,
, ![]() (3)
(3)
![]() ,
, ![]() (4)
(4)
![]() ,
, ![]() (5)
(5)
Cost Minimization Model. The objective of this model is to minimize the operation cost of all the public logistics nodes. In the view of the cost, analyzing the effect factors, establishing the objective function, finally getting the location decision which has the minimum operation cost.
Effect Factors on Cost. Public supply chain mode coordinates, manages and controls each link of non-core business in the view of regional industry, as it is shown in Fig.1.
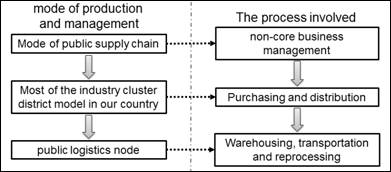
Fig.1 Link analysis involving
Considering the construction and operation cost of the public logistics node, the economic factors that have effect on its location were listed in Table 2.
Table 2 Table of economic indicators
|
Economic Indicator |
Effect Factors |
|
Transportation expenses from enterprise to logistics node |
Product properties |
|
Product freight rate |
|
|
The distance from enterprise to logistics node |
|
|
Transportation expenses from logistics node to entrance-exit |
Transport capacity in logistics node |
|
Freight volume |
|
|
The distance from logistics node to entrance-exit |
|
|
Managed fixed cost |
Number of employees |
|
Local wage level |
|
|
Logistics node scale |
|
|
Product administration expense |
Number of product |
|
Management level of logistics node |
|
|
Product handling fee |
Number of product |
|
Handling capacity in logistics node |
|
|
Construction cost |
Local price of land |
|
Geographical condition |
Method of Model and Assumption. The option location of the logistics node is known, and the number of logistics node is limited. The transportation expense is only related to the freight rates and distance from the enterprise to the public logistics node. An enterprise can only choose a public logistics node to serve for itself. The entrance-exit of cluster district is known, and its number is limited. Regardless of the differences between products in counting process. The cycle to calculate the operation cost of industry cluster district is 1 year.
Establishment of Cost Minimization Model.
Xik——The freight volume from enterprise k to public logistics node i.
Ydi——The freight volume from public logistics node i to entrance-exit d.
I——The set of all the newly-built public logistics nodes.
D——The set of the entrance-exit of the industry cluster district.
K——The set of enterprise in industry cluster district.
Ii=![]()
![]() =
=![]()
Cik(*)——The freight fare from k to i, it is a function of the transport unit price and the distance.
Cdi(*)——The freight fare from i to d, it is a function of the transport unit price and the distance.
NIi——The unit construction investment of newly-built public logistics node i, which is calculated by dividing basic investment by service life. i![]() I;
I;
gi——The unit handling fee when product flowing through logistics node i.
Fi——The fixed administration expense at public logistics node i.
Ai——The carring capacity of public logistics node i.
![]() ——The number of public logistics nodes that can be included by industry cluster district.
——The number of public logistics nodes that can be included by industry cluster district.
The cost at public logistics nodes is divided into 4 parts: basic construction investment, the transportation expenses from enterprise to logistics node, then to the entrance-exit of the industry cluster district, the reproducing fee at the industry cluster district, the management expense for products and the fixed management expense for public logistics nodes. So the objective function of the location model is:
![]()
![]() , i=1,2,3…
, i=1,2,3… ![]() , i=1,2,3…
, i=1,2,3… ![]() ; (6)
; (6)
Empirical Analysis. The auto industry park we studied on is located in the southwest of China, with a total area of about 37.7 square kilometers. The characteristic of its industrial concentration is obvious. Some data is shown in Table 3 and Table 4.
Table 3 Enterprise information table
|
enterprise |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
freight volume (ton) |
170000 |
510000 |
680000 |
1360000 |
170000 |
170000 |
|
freight rates (yuan/ton-km) |
0.15 |
0.14 |
0.14 |
0.13 |
0.15 |
0.15 |
Table 4 Public logistics node table
|
public logistics node |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
construction cost |
414400000 yuan |
425000000 yuan |
417200000 yuan |
421000000 yuan |
|
Product handling rates |
8 yuan/ton |
6 yuan/ton |
7 yuan/ton |
7 yuan/ton |
|
managed fixed cost |
4330000 yuan |
5410000 yuan |
4920000 yuan |
4600000 yuan |
Result of Sustainable Development Evaluation Model. The end result:
SD(the dispersive management)=0.5×23.2/4+0.3×19.6/5+0.2×24.6/6=4.896
SD(the cluster management)=0.2×28/4+0.4×41.1/5+0.4×43.2/6=7.592
According to the data, public logistics nodes in the districts make the sustainability evaluation of quantitative result greater than the dispersive management model, which increase the benefit of economy, society and environment.
Result of the Location Model. Using matlab code based genetic algorithm arriving at site-selection scheme about the public logistics nodes in automobile electromobile industry park is:Public logistics node 3 is selected in the four alternative nodes with operating costs 469405 thousand yuan. It is in accordance with experts results and actuality.
Conclusions
By using the location model of public logistics node, the public logistics nodes could be built in an industry cluster district. It can effectively reduce the empty driving, increase the using of the warehouse and save soil resources. The whole level of industry cluster districts in our country could be obviously improved, when the idea of public logistics nodes is popularized.
References
[1] Luoyan Li,Kuanghui Li,Wenzheng Yang. [J]. Henan Building Materials,2012,(2):146-150.
[2] Lijuan Ma. [J]. Market Modernization, 2008,(5):138-139.
[3] Yaping Zou. [J]. Digest of Management Science,2011,(16):46..
[4] Chen Wang. [J]. Zhejiang Today,2012, (22):34-35.




